The Present Value of a Perpetuity Can Be Determined by:
What is Perpetuity?
Perpetuity in the fiscal system is a situation where a stream of greenbacks menses payments continues indefinitely or is an annuity that has no finish. In valuation analysis , perpetuities are used to find the present value of a company'due south future projected cash flow stream and the company's terminal value . Essentially, a perpetuity is a series of greenbacks flows that keep paying outforever.
Finite Present Value of Perpetuity
Although the total value of a perpetuity is space, it comes with a limited present value . The present value of an infinite stream of greenbacks flow is calculated by adding upwards the discounted values of each annuity and the decrease of the discounted annuity value in each period until it reaches close to nix.
An analyst uses the finite present value of perpetuity to determine the exact value of a company if it continues to perform at the same rate.
Existent-life Examples
Although perpetuity is somewhat theoretical (tin can anything really last forever?), classic examples include businesses, real estate, and certain types of bonds.
One example of a perpetuity is the UK's government bond known every bit a Consol. Bondholders volition receive annual fixed coupons (interest payments) every bit long as they hold the amount and the government does not discontinue the Consol.
The second example is in the real-estate sector when an owner purchases a belongings and then rents information technology out. The owner is entitled to an infinite stream of cash flow from the renter as long as the holding continues to exist (bold the renter continues to rent).
Another real-life case is preferred stock, where the perpetuity calculation assumes the company volition go on to be indefinitely in the market place and keep paying dividends.
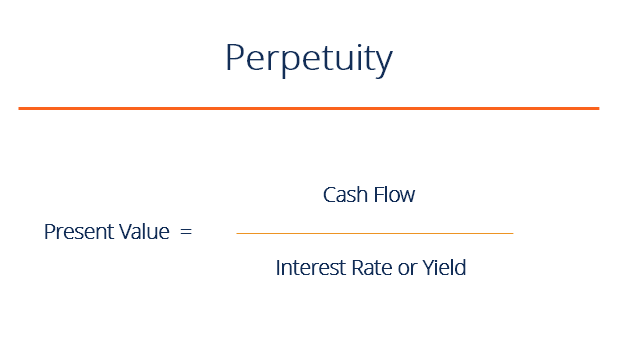
Present Value of Perpetuity Formula
Hither is the formula:
PV = C / R
Where:
- PV = Present value
- C = Amount of continuous cash payment
- r = Interest rate or yield
Instance – Summate the PV of a Abiding Perpetuity
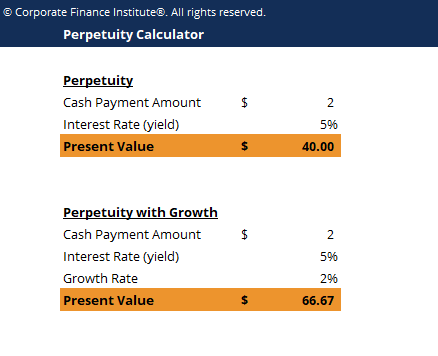
Visitor "Rich" pays $2 in dividends annually and estimates that they volition pay the dividends indefinitely. How much are investors willing to pay for the dividend with a required rate of return of 5%?
PV = ii/five% = $40
An investor volition consider investing in the company if the stock price is $40 or less.
Download the Gratuitous Template
Enter your proper name and email in the class beneath and download the costless template now!
Perpetuity Calculator
Download the free Excel template now to advance your finance knowledge!
Perpetuity with Growth Formula
Formula:
PV = C / (r – one thousand)
Where:
- PV = Present value
- C = Corporeality of continuous cash payment
- r = Involvement rate or yield
- g = Growth Rate
Sample Calculation
Taking the above example, imagine if the $2 dividend is expected to grow annually by 2%.
PV = $2 / (five – 2%) = $66.67
Importance of a Growth Charge per unit
The growth model is important for some final value calculations in the discounted cash flow model. The last, or terminal year, in the DCF model , volition be assumed to abound at a abiding rate forever. This, in essence, means that the terminal year greenbacks flow is a continuous stream of cash flow.
Additional Resources
Thanks for reading this guide to perpetuities. To help on your journey, these additional CFI resources will be helpful:
- Valuation Methods
- Cost of Preferred Stock
- Market Risk Premium
- Debt Schedule
zimmermansumanducke.blogspot.com
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/perpetuity/
0 Response to "The Present Value of a Perpetuity Can Be Determined by:"
Enregistrer un commentaire